Main Body
13 PHOTONS CATALYZE
*It is easier to visual length than frequency.
*Wavelength determines how photons interact with matter.
(Though this is based on the Bohr atomic model, frequency resonance works too.)
p. 42
Whether a photon will be absorbed by an atom or rejected depends on whether its wavelength will fit (resonate) the orbit of an outer electron.
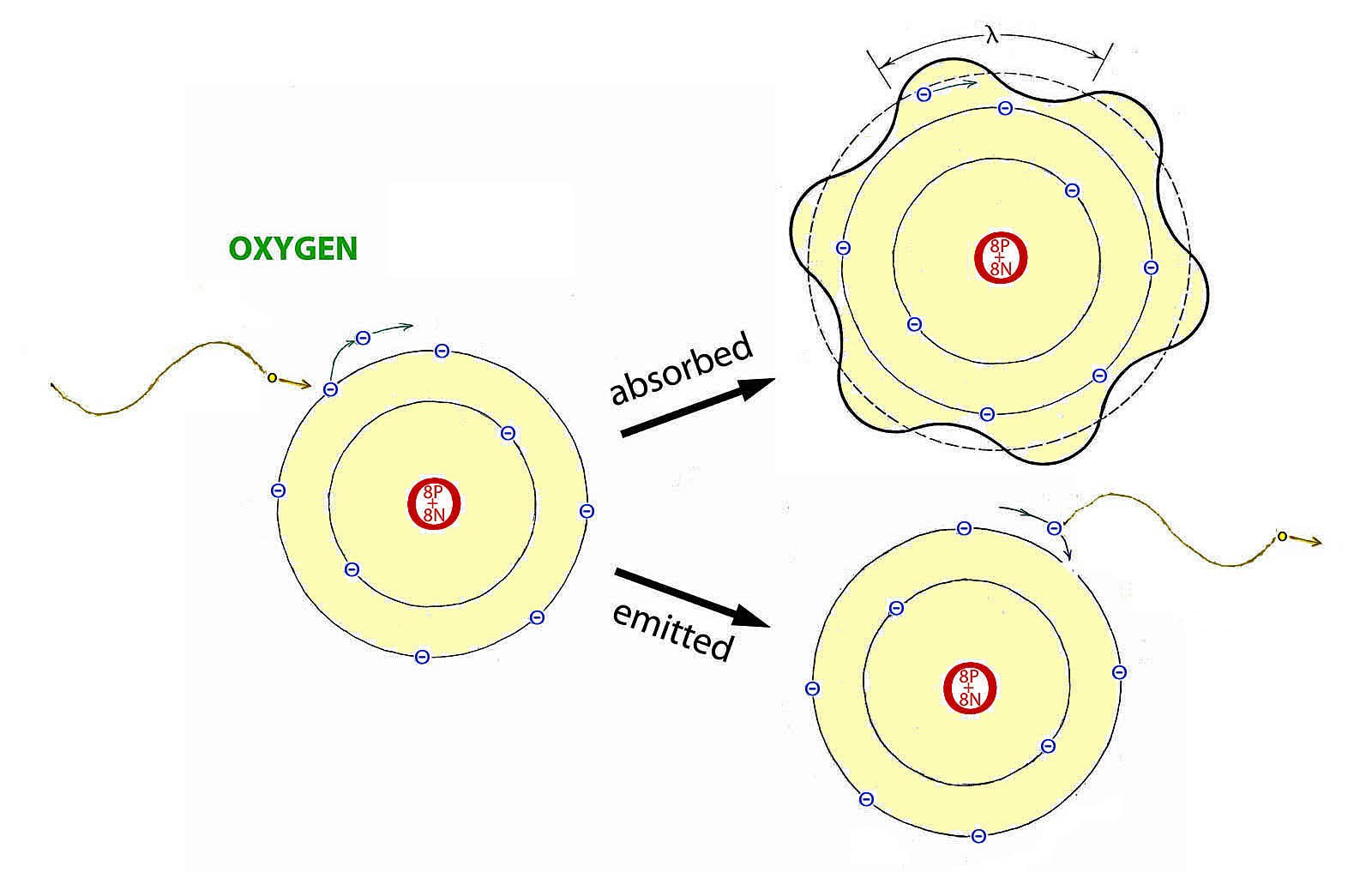
p.43
Atomic absorption of photons has a variety of consequences that range from slightly heating the substance to catalyzing changes in molecular structure. Depending on wavelength and substance such changes include:
*photosynthesis – photons trigger this chain reaction which oxygenates the earth’s atmosphere while simultaneously producing the ultimate energy source for most life.
*odorant release
*germicidal sterilization – including potential for non-medical containment of airborne viruses.7
*chromosome mutation
*photoisomerization – You are currently experiencing consequences of this effect:
Photons within a narrow range of the electromagnetic spectrum can be absorbed by specific molecules in the receptor cells of the retina.
This triggers a chain reaction that disrupts neurotransmitter release by these cells.
That in turn results in a series of nerve impulses which convey the effect of the image at that location.
Because such photons are our primary source of information about the world, they are accorded a special name:
